UI
-
CLI command-line / command interpreter
implemented in kernel (MS-DOS)
by systems program (Windows / UNIX)
multiple flavors implemented – shells UNIX / Linux
linux shell : shell: 带形参的批命令文件
-
batch interface
-
GUI graphical user interface
desktop, icon, Xerox PARC
system calls
Programming interface to the services provided by the OS
written in high-level language
Mostly accessed by programs via a high-level Application Program Interface (API) rather than direct system call use.
most common API:
- Win32 API
- POSIX API: for UNIX, Linux, and Mac OS X
- Java API: for JVM
A programmer accesses an API via a library of code provided by the operating system. (e.g. libc )
the run-time support system provides a system-call interface that serves as the link to system calls.
system call parameter passing
3 methods:


types of system call
-
process control
dump memory if error, Debugger for determining bugs, single step execution, Locks for managing access to shared data between processes
-
file manipulation
-
device manipulation
-
information maintenance
-
communications
-
message passing model
through an interprocess-communication facility (IPC) provided by OS
-
-
shared memory passing
process use map memory system call to gain access to regions of memory owned by other processes.
system prorams
file management
status information: Some systems implement a registry, used to store and retrieve configuration information.
file modification
programming-language support
program loading and execution
communications
system utilities/application programs:
background services: Launch at boot time. Run in user context not kernel context. Known as services, subsystems, daemons
OS design and implementation
策略policy: 决定做什么,可能随时间位置改变,对资源分配很重要
机制mechanism: 决定怎么做,系统更需要通用机制
The separation of policy from mechanism allows maximum flexibility if policy decisions are to be changed later. 微内核把机制与策略的区分利用到极致。
Emulation can allow an OS to run on non-native hardware.
用高级语言编写, OS更易移植,降低速度,增加存储要求
bottleneck routines can be identified. replaced with assembly-language equivalents.
OS structure
-
simple structure
-
MS-DOS
没被仔细划分成模块,没有很好区分接口和层次
-
UNIX
由内核和系统程序组成
-
-
layered approach
the bottom layer (layer 0) is the hardware, the highest (layer N) is the user interface
每层利用低层提供功能实现
advantage: contruction, debugging, design, implementation
difficulty: disk driver & memory-management routines, disk driver & CPU scheduler
less efficient
-
microkernels
Mach
microkernel contains only essential functions
- memory management
- CPU scheduling
- communications
微内核主要功能:使 客户程序 和 运行在用户空间的各种服务 之间进行通信 message passing
Mach, Tru64 UNIX, Mac OS X kernel, QNX
由于系统功能总开销增加而导致系统性能下降
-
modules
Many modern operating systems implement loadable kernel modules.
The kernel has a set of core components and dynamically links in additional services via modules, either at boot time or during run time.
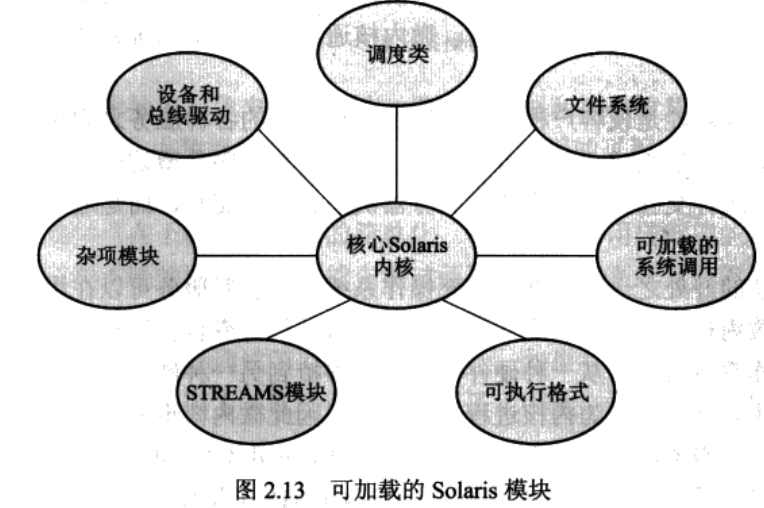
允许内核提供核心服务,也能动态地实现特定功能
类似分层,但更灵活,任一模块可调用其他任何模块。
类似微内核,核心模块只有核心功能及其他模块加载和通信的相关信息。更高效,因为模块无需调用消息传递来通信。
hybrid systems:
linux & solaris: monolithic, modular
windows: monolithic, plus microkernel for different subsystem personalities, run as user-mode processes, dynamically loadable kernel modules
Mac OS X: 分层,其中一层包括Mach微内核
virtual machines
takes the layered approach to its logical conclusion
It treats hardware and the operating system kernel as though they were all hardware.
The operating system creates the illusion of multiple processes, each executing on its own processor with its own (virtual) memory.
- by CPU scheduling
- by virtual memory
virtualization: a technology that allows operating systems to run as applications within other operating systems. VMM(virtual machine Manager)
Emulation used when source CPU type different from target type. When computer language not compiled to native code – Interpretation
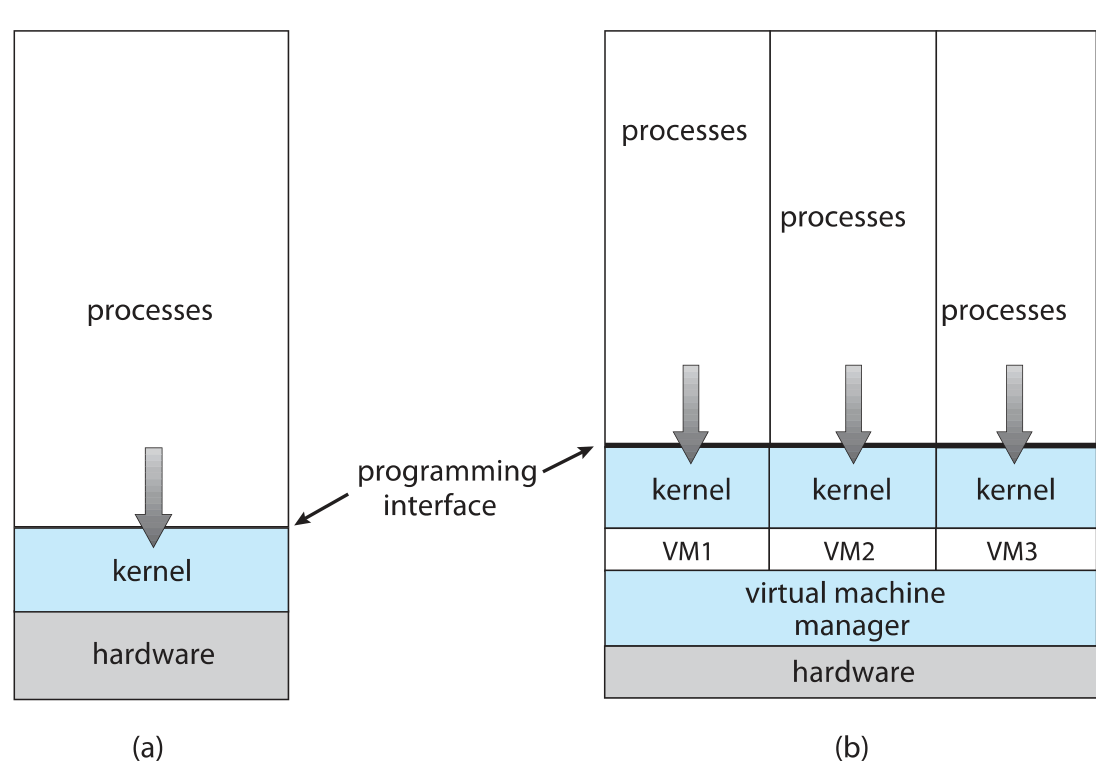
advantage: protection of system resources, solving system compatibility problem.
虚拟机软件允许在kernel mode(因为它自己就是操作系统),但虚拟机自身只能允许在user mode
virtual kernel mode 和 virtual user mode 都允许在 physical user mode
真正机器上user mode到kernel mode的切换,也必须在虚拟机上引起从virtual user mode到virtual kernel mode的切换
JVM
consists of
-
class loader
-
class verifier
-
Java interpreter
software module that interprets the bytecodes one at a time
- Just-In-Time (JIT) compilers turns the architecture-neutral bytecodes into native machine language for the host computer.
JVM automatically manages memory by performing garbage collection.
OS generation
对于某个特定的计算场所,必须配置configure和生成generate系统:SYSGEN
generation methods:
可完全重新编译
或系统描述可用来创建表
或完全table-driven(绝大多数现代OS是这样),选择发生在执行时而不是编译连接时。
system boot
booting: starting a computer by loading the kernel
Bootstrap program (bootstrap loader): small piece of code stored in ROM. locates the kernel, loads it into memory, and starts its execution.
two step:
-
bootstrap loader
fetches the boot program from boot block into memory to execute.
-
boot program
loads the entire OS into memory and begin its execution
最后修改于 2020-02-28